Surgery takes years of intensive studio and stable hand for humans, but robots may have easier time to lift it with today’s AI technology.
Scientists at Johns Hopkins University (JHU) and Stanford University taught a robotic surgical system to perform a lot of surgical tasks as a hood as human doctors, simply training it in the video of these procedures.
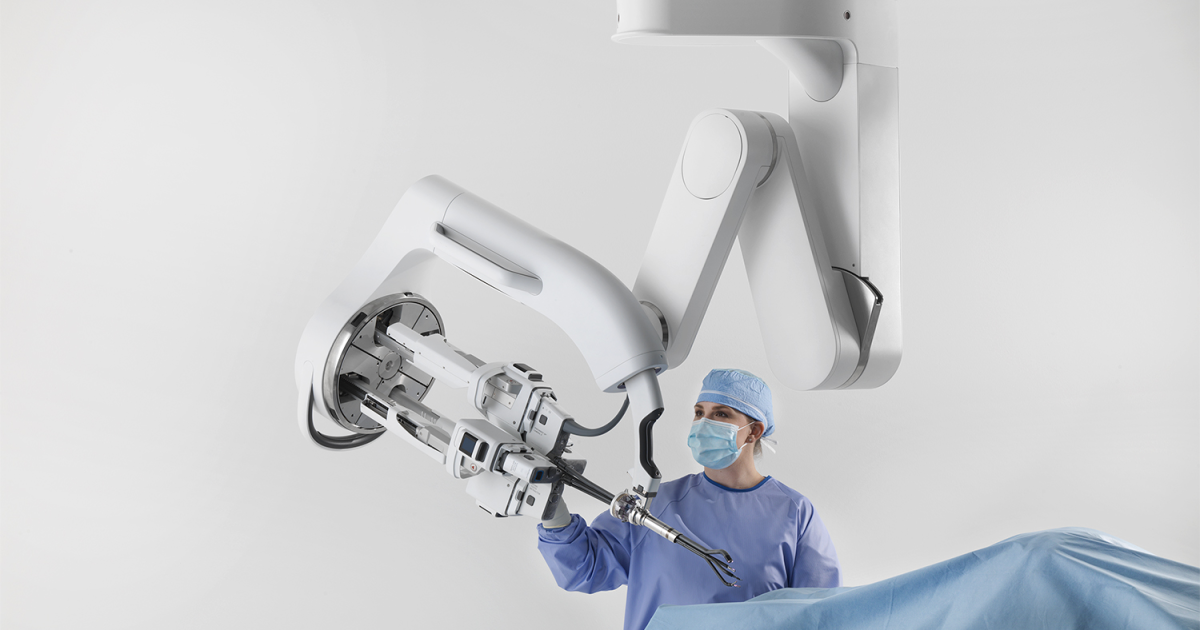
The team uses the Surgical System DA Vinci for this study. It is a robotic system that is usually remotely controlled by a surgeon with weapons that manipulates tasks such as an autopsy, subcment and cutting and seals. Surgeons, such as these, give surgeons much more control, accuracy and a closer look at patients on the operating table. It is estimated that the latest version is worth $ 2 million, and this does not include accessories, sterilization facilities or training.
Intuitive
Using the machine learning method known as imitation learning, the team trained the Surgical System DA Vinci to perform three tasks in surgery independently: handling the needle, lifting body tissue and sewing. Also looks.
Demo Surgical Robot Transformation
The surgical system not only made a man, but also learned to correct his own mistakes. “As if it dropped the needle, it will pick it up automatically and continue. This is not something I have learned, ”said Axel Krieger, Associate Professor at JHU, co -authored by a documentary about the findings of a team that was presented at a conference on this week about robot learning.
Scientists have trained AI model by combining learning imitation with machine learning architecture, which builds popular chatbots as a chatgpt. Although these cottages are designed to work with the text, this model spits kinematics – a language used to describe movement with mathematical elements and equations – to direct weapons of the surgical system.

Intuitive
The model was trained using hundreds of videos recorded from the wrists on the Da Vinci Robots during surgery.
The team believes that its model could train a robot to quickly perform any type of surgery, and much easier than the traditional manual coding method of every step needed to surgery actions.

University / Stanford University Johns Hopkins University
According to Krieger, this could help do an automated surgery by reality before we could propose before. “What is new here is that we just have to collect the imitation of learning different procedures and we can train a robot that read it in a few days,” he said. “It allows us to accelerate the target of autooms while reducing medical errors and achieving more accurate surgery.”
This could be one of the largest breakthroughs in the world of surgery based on robots in recent years. There are several automated devices for use in complex operations, such as Corindus Corpath for cardiovascular procedures. However, their capacity is usually limited to certain steps of Superdies they help with.
Furthermore, Krieger pointed out that the coding of every step for the robotic system could be terribly slow. “Someone could spend ten years attempt to model sewing,” he said. “And this is sewing only for one type of operation.”
Krieger also worked previously to be of different consent to automate surgical tasks. In 2022, his team of scientists developed an autonomous robot or star, on a yh. The robot, led by a three -dimensional endoscope based on structural light and machine -based, robot, the robot together sewed two ends of the intestine without human intervention.
Scientists are now working on a robot training with their learning method of learning to perform full surgery. It will probably be years before we see how robots fully transport for surgeons, but innovations, such as this one that is complex to treat the safer and accessible to patients around the world.
Source: Johns Hopkins University